Understanding Course Details
Course Codes
All courses have a unique code made up of the subject code and the catalogue number.
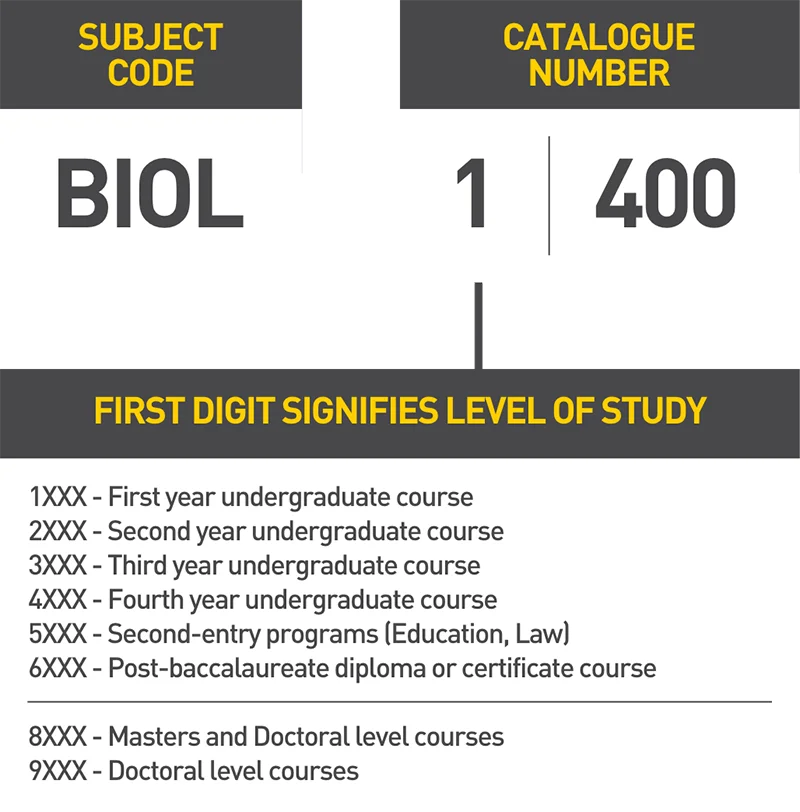
Subject Codes
Subjects
- ACCT - Accounting
- ACSC - Actuarial Science
- AERO - Aeronautics
- ANZO - Anthrozoology
- ARAB - Arabic Studies
- ARGU - Argumentation Studies
- ARHS - Art History
- ARSC - Interdisciplinary Arts and Science
- ARTX - General Arts Exchange
- ASIA - Oriental Studies
- BIOC - Biochemistry
- BIOL - Biology
- BSMM - Business - Master of Management
- BUSI - Business
- BUSN - Business Elective
- BUSP - Business - Professionals & Mngrs
- BUSR - Business Research
- BUSX - Business Exchange
- CASJ - Communication and Social Justice
- CBMI - Cross Border Mgmt & Intl Trade
- CDNS - Canadian Studies
- CHEM - Chemistry
- CIVL - Civil Engineering
- CMAF - Communication, Media and Film
- COMP - Computer Science
- DIAS - Diaspora Studies
- DIGJ - Digital Journalism
- DISB - Disability Studies
- DRAM - Dramatic Art
- ECON - Economics
- EDUC - Educ Org Learning & Teaching
- EENV - Earth & Environmental Science
- ELEC - Electrical Engineering
- ENGL - English Language & Literature
- ENVE - Environmental Engineering
- ESCI - Earth & Environmental Science
- ESTU - Environmental Studies
- FILM - Film Production
- FINA - Finance
- FREN - French Studies
- FRSC - Forensic Science
- GART - General Arts
- GENG - General Engineering
- GENX - Engineering Exchange
- GLIE - Environmental Science
- GREK - Greek Language and Literature
- GRHS - Greek and Roman History
- GRMN - German Language Option
- GRST - Greek and Roman Studies
- HIST - History
- HKEX - Human Kinetics Exchange
- HUGR - Human Geography
- HUMK - Human Kinetics
- INCS - Intercultural Studies
- INDE - Industrial Engineering
- ITLN - Italian Language Option
- JWST - Jewish Studies
- KINE - Kinesiology
- LATN - Latin Language and Literature
- LAWD - Dual Canada/US JD
- LAWG - Law
- LAWM - Law Masters
- LAWS - Law Service
- LAWX - Law Exchange
- LING - Lingustics
- MACS - Media Arts and Culture
- MATH - Mathematics
- MATL - Engineering Materials
- MECH - Mechanical Engineering
- MGMT - Management and Labour Studies
- MKTG - Marketing
- MSCI - Management Science
- MUSC - Music Academic Studies
- MUSP - Music Performance Studies
- NURS - Nursing
- NURX - Nursing Exchange
- PGEO - Physical Geography
- PHIL - Philosophy
- PHYS - Physics
- POLS - Political Science
- PROE - Professional Elective
- PSYC - Psychology
- RESG - Graduate Research
- SACR - Sociology, Anthropology, Criminology
- SCIE - General Science
- SCIX - Science Exchange
- SJST - Social Justice
- SOSC - General Social Science
- SPAN - Spanish Language Option
- STAT - Statistics
- STEN - Strategy & Entrepreneurship
- SWRK - Social Work
- VABE - Visual Arts - Built Environment
- VSAR - Visual Arts
- WGST - Women's and Gender Studies
- WORK - Work Employ Issues
Section
Indicate the specific section in which you are registering. Section codes 51 – 84 normally are reserved for laboratory sections associated with a particular lecture. In some cases, students MUST ALSO REGISTER FOR A LAB SECTION. Otherwise, labs are arranged by the department or instructor once classes have begun.
Units / Credit
- 0.00 Non-credit activity, such as a lab.
- 1.50 Semester half-course.
- 3.00 Regular Semester Course. Some 3.00 unit courses may be offered over two semesters.
- 6.00 Normally a two-semester course or a single-semester, double-unit intensive language training course.
Class Days
- M - Monday
- T - Tuesday
- W - Wednesday
- R - Thursday
- F - Friday
- S - Saturday
- U - Sunday
Need help?
The University of Windsor Undergraduate Calendar is your source for official information about the undergraduate academic programs and regulations of the University of Windsor.
If you’re having a hard time figuring out which courses to take or if you’re not sure if you’re on the right track reach out to us for help. Talk to an academic advisor if you have program specific questions, and for general inquiries you can ask.UWindsor.
Academic Calendars
The University of Windsor Academic Calendar is your source for official information about academic programs and regulations of the University of Windsor.
Registration Guides
Read our Step by Step Articles
Read through our many Knowledge Base Articles.
Watch our Step-by-Step Video
Watch a current UWindsor student guide you along.
Download our Step by Step PDF
Download, print and read our pdf guide.